mhc class ii deficiency
MHC Class II deficiency. T cells are then unable to proli.

Mhc Class Ii Cell Autonomously Regulates Self Renewal And Differentiation Of Normal And Malignant B Cells Sciencedirect
Terms in this set 14 What are 3 effector T cells CD4 T cells differentiate into.

. Pathogenesis is based on a deficiency in MHC class II molecules being present on antigen presenting cells such as macrophages B cells and dendritic cells. MIM 209920 first described in the late 1970s. Immunodeficiency by defective expression of HLA class 2 is a rare primary genetic immunodeficiency disorder characterized by partial or complete absence of human leukocyte antigen class 2 expression resulting in severe defect in both cellular and humoral immune response to antigens.
MHC class II deficiency is a rare primary autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder PID. PubMed is a searchable database of medical literature and lists journal. 1 Four disease-causing genes.
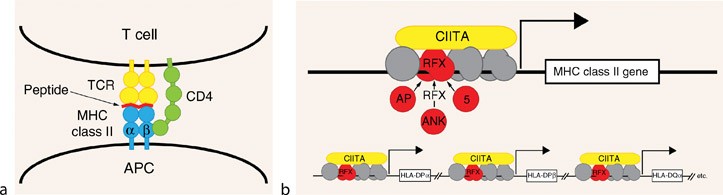
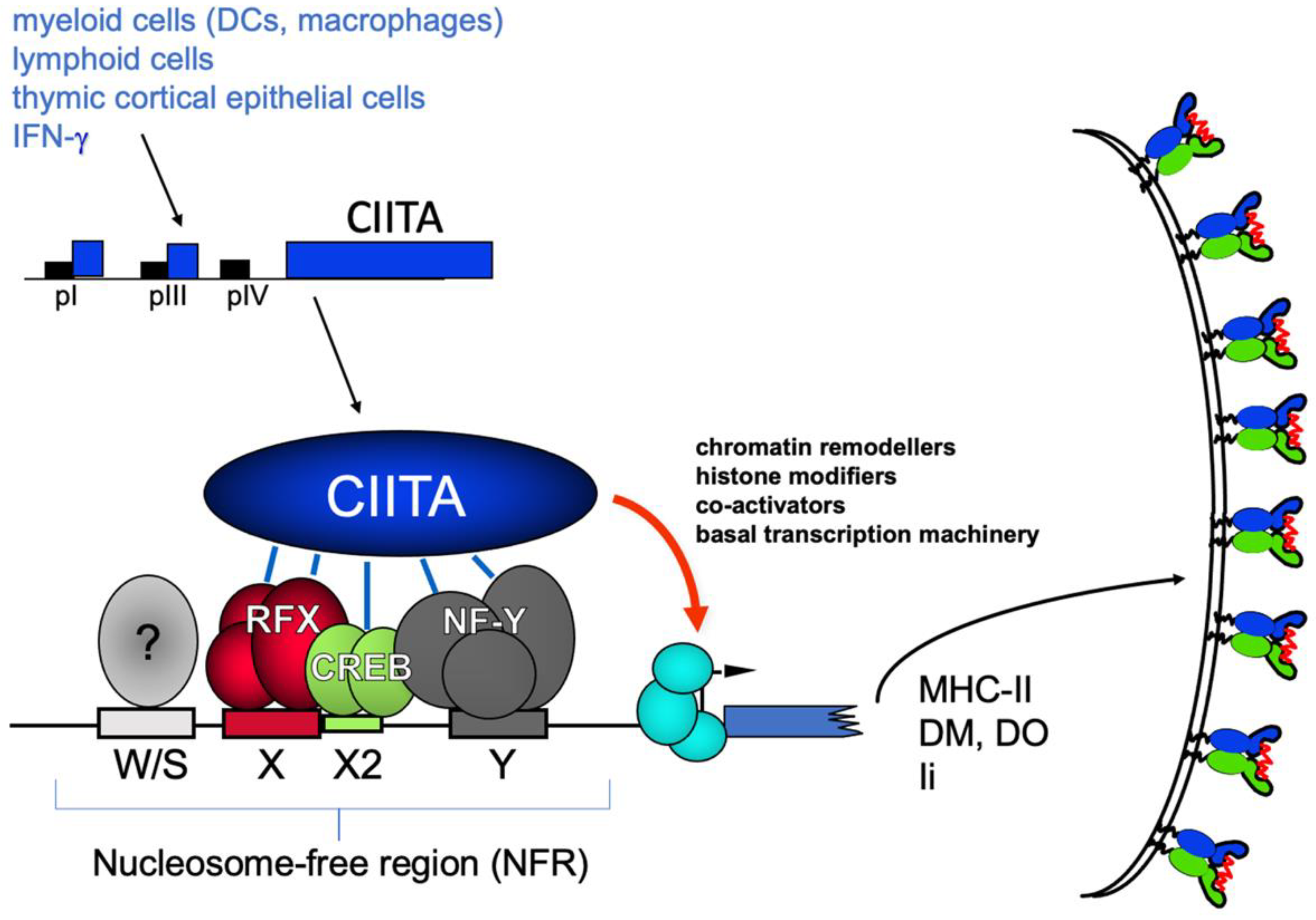
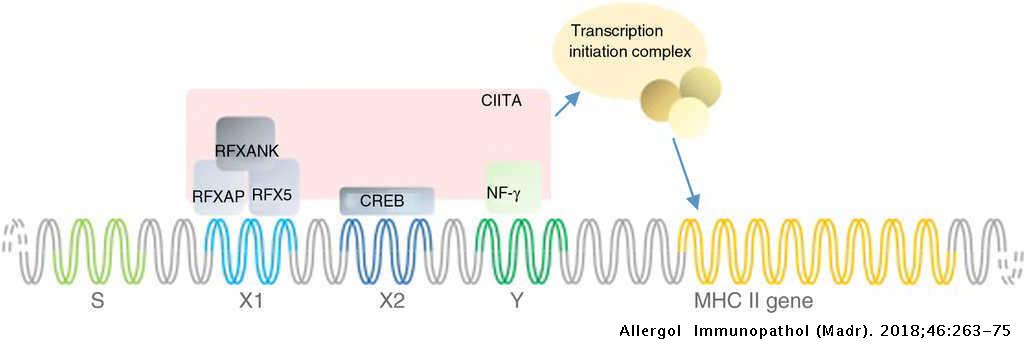
MHC class II deficiency. Deficient MHC class II molecules are unable to present antigens to T cells and properly activate T cells. 1 Somatic fusion experiments led to the description of 4 complementation groups A B C and D.
Diagnosis definitive diagnosis is accomplished with. One type of MHC class II deficiency also called bare lymphocyte syndrome is due to mutations in the genes that code for transcription factors that regulate the expression of the MHC class II genes. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man OMIM is a catalog of human genes and genetic disorders.
Biomedical Research Reagents Are Cited In Over 360000 Publications. The phenotype is similar to SCID and susceptibility to infection by viral bacterial fungal and protozoal agents is. The list of signs and symptoms mentioned in various sources for MHC class 1 or class 2 deficiency includes the 12 symptoms listed below.
Each entry has a summary of related medical articles. Impaired transcription of the MHC class II genes has been shown to account for the lack of expression of DR DP and DQ MHC class II proteins on APCs. Ad MHC class II ER-TR3 Monoclonal Antibody Is Recommended For Detection Of MHC class II.
It is meant for health care professionals and researchers. Defects in transacting regulatory factors required for expression of MHC class II genes rather than the genes themselves are responsible for the disease phenotype. This is caused by a mutation in This is caused by a mutation in.
This syndrome is caused by mutations in transcription regulators of the MHC II. Normal number of T- and B-cells in the peripheral blood. MHC class II deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder which is seen most often in patients from around the Mediterranean Sea.
-Patients with 10 of normal MHC class I expression do not have an increased incidence. Class II major histocompatibility complex MHC deficiency called bare lymphocyte syndrome is a rare heterogeneous group of autosomal recessive diseases in which patients express little or no HLA human leukocyte antigen-DP HLA-DQ or HLA-DR on B lymphocytes macrophages and DCs and fail to express class II MHC molecules in response to IFN-γ. The disease is primarily characterized by the absence of MHC class II.
As described below the phenotype of MHC-II-knockout mice is very similar to that of the human MHC-II deficiency known as bare lymphocyte syndrome type II BLS. MHC class II deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease also known as bare lymphocyte syndrome type II. The disease spectrum is quite broad ranging from asymptomatic to severe.
This immunodeficiency presents with a more severe phenotype than MHC class I deficiency. Patients presents early in infancy with a mild form of severe combined immunodeficiency SCID as they have increased susceptibility to pyogenic and opportunistic infections. This immunodeficiency is typically milder than MHC class II deficiency.
They express normal or only. What is the function of Th1 Helper T cells. MHC class I deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease also known as Bare lymphocyte syndrome type I.
MHC class II deficiency major histocompatibility complexMHCII deficiency is a rare deficiency of MHC class II molecules and ultimately to a disruption of gene regulation. Persistent diarrhea Malabsorption Mucocutaneous candidiasis Upper respiratory tract bacterial infection Lower respiratory tract bacterial infection Failure to thrive Chronic sinusitis Chronic bronchitis Fatigue Viral. A genetic disorder caused by molecular defects in the genes encoding for four regulatory factors controlling transcription of MHC class II genes.
The MHC locus itself is intact in patients with MHC class II expression deficiency. It results in the depletion of CD4 T cells and some immunoglobulin isotypes even though there are normal levels of both CD8 Cells and B cellspresent. MHC class II deficiency is a prototype of a disease of gene regulation.
Absence of MHC class II on B cells CD4 T-cells. Approximately 100 patients with this disease have been reported to date. MHC class II molecules are pivotal for the adaptive immune system and guide the development and function of CD4 T-lymphocytes.
The result is that the immune system is severely compromised and. The bare lymphocyte syndrome type II BLS II is a rare recessive genetic condition in which a group of genes called major histocompatibility complex class II MHC class II are not expressed. The MHC II deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency syndrome with increased susceptibility to respiratory and gastrointestinal infections failure to thrive and early mortality.
Differential other immunodeficiency syndromes such as SCID. Ii Invariant chain deficiency Since Ii plays an essential role in the assembly and transport of nascent MHC-II lack of Ii in Ii-knockout mice severely disrupts MHC-II synthesis. OMIM is maintained by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
MHC class II deficiency is a rare primary autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder PID. Th1 Th2 and Treg. MHC class II plays an important role in the maturation and functioning of T- and B-cells.
MIM 209920 first described in the late 1970s. The disease is primarily characterized by the absence of MHC class II molecules on the surfaces of immune cells. Major histocompatibility complex MHC class II deficiency also known as bare lymphocyte syndrome type II is a rare autosomal recessive combined immunodeficiency and was first described in 1980s.

Tumor Regulation Of Distal Mhc Class Ii ϫ Splenic Macrophage Download Scientific Diagram
Mhc Class Ii Deficiency Springerlink
Ijms Free Full Text The Mhc Class Ii Transactivator Ciita Not Quite The Odd One Out Anymore Among Nlr Proteins Html

Lrr Dependent Nuclear Localization Of Ciita And Mhc Ii Transac Download Scientific Diagram
Mhc Class Ii Deficiency Report Of A Novel Mutation And Special Review Allergologia Et Immunopathologia

Hla Dm An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Major Histocompatibility Complex Class Ii Abbey Jones Ppt Download

Targeted Complementation Of Mhc Class Ii Deficiency By Intrathymic Delivery Of Recombinant Adenoviruses Immunity

Mhc Ii Molecules In Inflammatory Diseases Interplay Of Qualities And Quantities Trends In Immunology

Mhc Class Ii An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome Definition Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Induction Of Mhc Class I Expression By The Mhc Class Ii Transactivator Ciita Immunity

References In Mhc Class I And Ii Deficiencies Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

The Location Of The Tap Genes In The Human Mhc Class Ii Complex Hla Download Scientific Diagram

A Genome Wide Multidimensional Rnai Screen Reveals Pathways Controlling Mhc Class Ii Antigen Presentation Cell